IN THIS LESSON
Have you ever snapped at someone over something tiny and later thought, “Yikes…that was dramatic..😬”?
Or maybe you’ve spent hours replaying awkward conversations in your head at 2 AM (hey..we’ve all been there).
Or you suddenly remember something painfully embarrassing, and you just want to pull a full-on Cinderella meltdown—ugly-cry, sprint away, and become invisible to the rest of the world (again…we’ve all been there 😭)
Turns out, your brain is basically a complicated roommate—it's always doing stuff you don't fully understand.
Stay tuned—psychology is about to pop the hood on your brain and decode every midnight cringe replay. 🧠✨
First Things First: What Even IS Psychology?
Psychology is the science of human behavior and mental processes.
In other words, it helps us figure out why we act, think, and feel the way we do.
Vocab Check
-
Stuff we do that’s observable. like giving someone candy or blushing when your crush walks by. It can be voluntary (planned actions) or involuntary (automatic reactions like heart racing when you’re nervous).
-
The stuff going on in your mind. Thoughts, beliefs, memories, feelings, all that inside stuff.
Quick Check in! 🧠
Which of these is a “behavior” and NOT a “mental process”?
-
Pizza sounds fire rn..yes…but it’s not the correct answer to the question.
Why not A? Day‑dreaming about a yummy slice is totally inside your head—no outward signs unless you start drooling. That’s a mental process.
-
Your heart racing is an observable behavior—anyone with a pulse monitor could see it.
-
Why not C? Replaying your personal cringe snap video is also internal. Nobody else can peek at those reruns, so it stays a mental process.
-
B! Your heart racing is an observable behavior.
So wait..psychology is a science??
Yup! Every branch of psych has to prove its claims with empirical evidence (aka data you can measure, replicate, and peer‑review).
Whether you’re studying toddlers or neurotransmitters, you still follow the scientific method: ask a question, design a study, collect numbers, run stats, cry over Excel, hit “publish.”
Different zoom levels, same nerdy mission—figuring out why Homo sapiens act the way we do. They might finger‑gun each other for clout, but they all fire peer‑reviewed papers and play by the same scientific rules.
Vocab Check
-
Basic ideas that help us organize thoughts. (Think: Categories like "pets" or "snacks".)
-
General statements explaining how things usually work.
-
Sets of concepts and principles that explain or predict behavior.
Quick Check-in! 🧠
If I say "An apple a day keeps the doctor away," is that a...
-
Why not A? A concept is just a mental bucket, like “fruit” or “self‑care Sundays.” It labels stuff; it doesn’t claim anything will happen.
-
It’s a principle—a general statement about how things usually work.
-
Why not C? A theory is a big-picture framework that ties multiple principles together and makes testable predictions—think "Germ Theory" or "Attachment Theory." Our apple proverb doesn’t have that kind of scientific scaffolding.
-
B! It’s a principle—a general statement about how things usually work.
First Perspectives
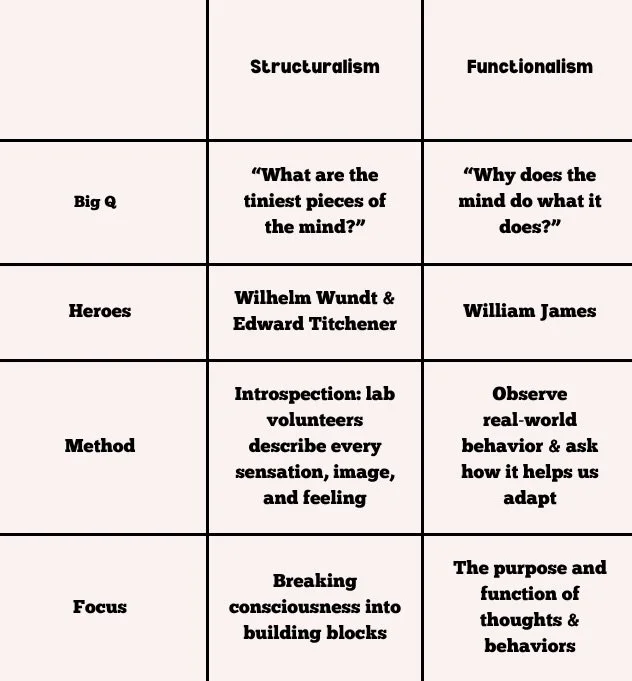
Structuralism vs. Functionalism—The Original Psych Throwdown
Quick Translation:
-
zooming in on each pixel of your mental selfie.
-
posting the selfie and asking, “How does this help my brand?”
Quick Check-in! 🧠
If you’re dissecting why your taste buds tingle when you eat Hot Cheetos, you’re a Structuralist. If you’re wondering why spicy snacks keep you munching even while your mouth is on fire, you’re a Functionalist.
Freud, Behaviorism, and Modern-Day Psychology.
Sigmund Freud
I know….I know….
just hear me out.
While there are a lot of different opinions on freud, his work played a huge role in shaping modern psychology.
Famous for his psychoanalysis (Talk therapy). He believed our childhood and subconscious minds affect ouR adult behaviors (some of his stuff though..pretty weird)
What’s Behaviorism?
Behaviorism: Believed psychology should only study observable actions. Behaviorists focused on how we leaRn from rewards and punishments (ever trained a pet? It’s like that).
Levels of Analysis: Bio, Psycho, Social
Psychologists examine issues from three main angles:
-
(brains, genes, evolution)
Quick Example Check!
If you get stressed over exams, psychologists might look at:
Biological: How stress hormones affect you
-
(thoughts, emotions, behaviors)
If you get stressed over exams, psychologists might look at:
Psychological: Your thought patterns around tests
-
( culture, environment, relationships)
If you get stressed over exams, psychologists might look at:
Social: Pressure from friends or family expectations
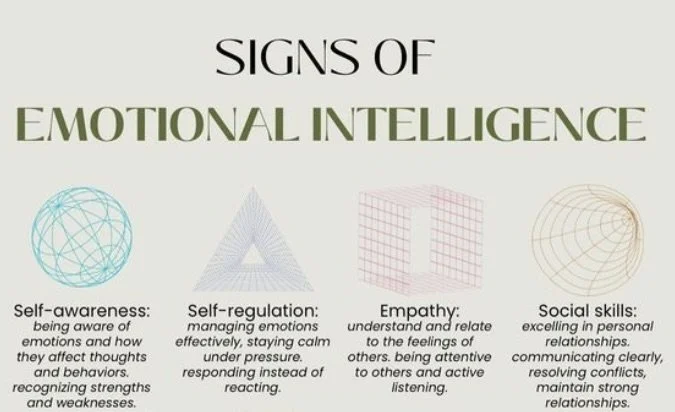
Emotional Intelligence (EI): Your Secret Superpower
EI is about recognizing, understanding, and managing emotions—yours and others’.
It’s basically why some people handle stress like absolute champs and others, well…don’t.
EI Skills to Master:
-
Knowing what you’re feeling
-
Managing your reactions (hello, patience)
-
Making thoughtful choices
-
Understanding others’ emotions
-
Navigating social interactions gracefully
Quick Check-in! 🧠
If your friend’s having a rough day and you immediately notice and offer comfort, that’s:
-
Why not A? Self-regulation is your own impulse control—like resisting the urge to rage‑tweet or binge a whole sleeve of Oreos. It’s inward, not outward.
-
Empathy is all about reading the vibes and showing up for someone’s feelings
-
Why not C? Ethical Judgment is weighing right vs. wrong ("Should I leak the group chat?" 👀). It’s a moral decision process, not an emotional radar.
-
Answer: B! Empathy is all about reading the vibes and showing up for someone’s feelings
So, WHY should you care about EI?
Because it’s linked to job success, better relationships, and overall happiness. High EI helps you stay calm under pressure, boosts your mental health, and makes you better at dealing with people in pretty much every area of life.
Boosting Your EI Game:
Journaling and mindfulness help build self-awareness.
Breathing exercises and setting clear goals improve self-regulation.
Practicing perspective-taking and active listening sharpens empathy and social skills.
Hey so…you just learned a lot of the basics of psychology. From its historical glow-up to emotional intelligence superpowers. Go ahead and flex that brain power—you’ve earned it!
Key Takeaways 📝
-
Every claim must survive the scientific method and peer review.
-
If you can see it or measure it externally, it’s behavior; if it’s only in your head, it’s mental.
-
Structuralism (break it down) vs. Functionalism (why does it matter?).
-
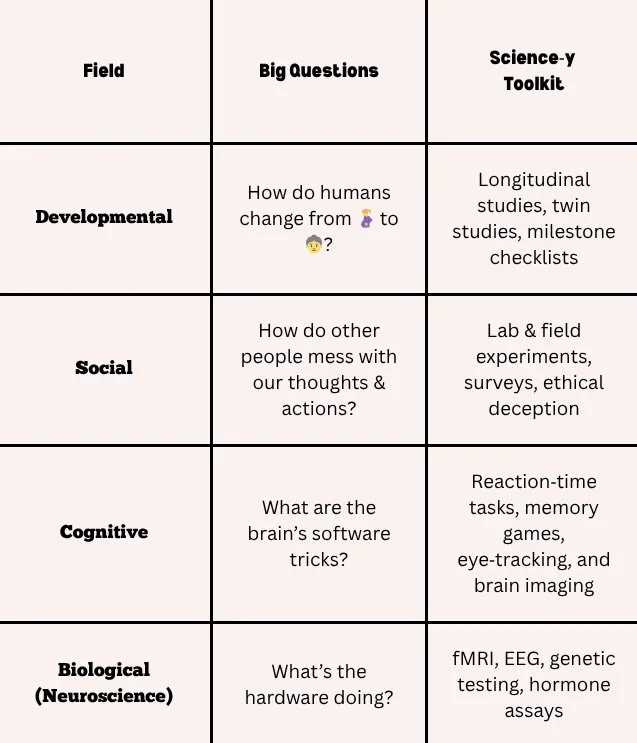
Developmental, Social, Cognitive, Biological, etc., all share the same empirical playbook.
-
Explaining behavior means zooming in (biology) and zooming out (social context).
-
Self‑awareness, self-regulation, empathy, ethics, social savvy = life upgrade.
Want More? 📚
Grab my full, unfiltered class notes (with extra examples and study tips) right here ➡️ Download the official PSY notes. Use them to your advantage! These notes come from the official SOOMO "Psychology in the Real World” textbook written by Jennifer Harper, PhD
References
Harper, J. (2024). Psychology in the real world (2nd ed.). Soomo Learning. https://www.soomolearning.com/courses/psychology-in-the-real-world